Modern Theory of inflation:
Definition:
Inflation
is a situation when price increase is Irreversible in the market .it is called
inflation.
Definition
in Money Market:
Inflation
is a condition of rise in the stock of money, under this situation to much
money chases to few goods.
Definition
in good market
Inflation
is the condition of generalized excess demand in the goods market.
Definition
in international market
Inflation is a fall in the external value of
money as measured by foreign exchange rate or by price of gold.
Classification/Types
of inflation
1. Open or suppressed inflation.
2. Creeping/moderate
3. Galloping/hyperinflation
4. Anticipated and unanticipated
5. Demand pull
6. Cost push
7. Administrative inflation
1. Open or suppressed inflation.
2. Creeping/moderate
3. Galloping/hyperinflation
4. Anticipated and unanticipated
5. Demand pull
6. Cost push
7. Administrative inflation
Criteria
for classification
1. Working of market
2. Rate of which price are increased
3. Expectation about inflation
4. Causes of inflation
1. Working of market
2. Rate of which price are increased
3. Expectation about inflation
4. Causes of inflation
Explanation
and definition of demand pull inflation what are its causes and remedies to
control it
Definition
of demand pull
Demand
Pull inflation is actually the
concept of classical economist. according to them demand pull inflation is a situation when aggregate supply remaining the same and aggregate demand is increased as shown in the diagram explanation in the above diagram
concept of classical economist. according to them demand pull inflation is a situation when aggregate supply remaining the same and aggregate demand is increased as shown in the diagram explanation in the above diagram
Figure 3.1
Explanation:
In
the above diagram AS and AD interest at point E0. At this point level of
employment P0 Is YF and level of price is P0. Now, if Aggregate Demand (AD)
increase it will be shift upward from AD0 to AD1 and new equilibrium point is
E1 level of employment remain same, but price level increase from P0 to P1 due
to increase in aggregate demand.
We can use IS-LM approach to explanation of demand pull
inflation.
Figure 3.2
Explanation: In the diagram three market equilibrium at
point E0 level of employment is YF and price level P0 if money supply increases
LM curve shift right down ward new equilibrium level of point E1 level of
employment determined by this point is YA which is above full employment level and
price determined in the market is 0P1.now it is clear that when money supply
increases in the country price level also increase. When price level increased
LM1/P0 shift upward left which shows that real purchasing power of peoples
decrease and LM1/P1 reach at point EO and this procedure is continuous until it
reach at point E3 at this point level of employment is YB which is below the
level of full employment price level also increased from 0P1 to 0P3 Smoothly.
Demand
pull inflation in Keynesian view
in Keynesian framework increase in demand will
not immediately bring an increase in price level but after a certain point man aggregate
supply (AS) curve become vertical straight line increase in demand will bring
an increase in price level. It will be called demand pull inflation or pure
inflation in Keynesian analysis as shown in figure 3.2
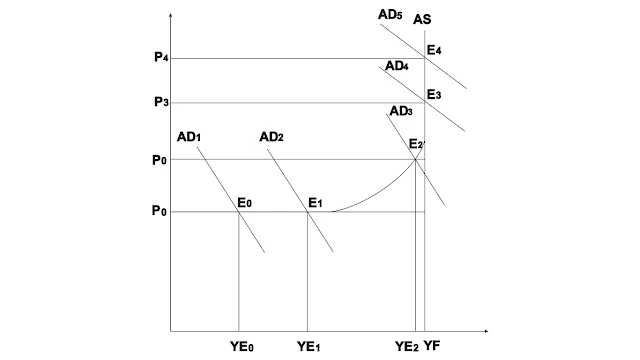
Figure 3.3
Explanation: in
this diagram according to Keynesian employment AD1 interest AS curve at point E0
equilibrium level of employment is YE0
and
price level is PO if a d curve shift right ward and intersect at point E1 level
of employment increase from YE0 To YE1 but price level remain same it is clear
that in first part AS curve if AD increase in this part level of employment
increase but price level remain constant and there will no inflation in first phase
of AS curve
2nd
in second phase of AS curve if ad increases and due to this change price also will
also change. We call it bottle neck inflation as shown in figure 3.2 above Ad2
shift to right upward and intersect at E2 at this point employment level
increase YE1 to YE2 price level goes up P0 to P2 in this part of is AS curve as
aggregate demand (AD) increased level of employment and price level will also increase.
According
to Keynesian model when we reach in 3rd phase of aggregate supply (AS) curve, The
demand pull inflation will create as aggregate demand (AD) increase and aggregate
demand (AD) curve will shift upward there will be no change in level of full
employment but there will be change in price level increased from P2 to P3 and
P4 as aggregate demand (AD) increase continuously
Causes
of demand pull inflation
1. Increase in the population
1. Increase in the population
As
population of a country increase there will be an increase in the effective demand
and due to this increase in effective demand price level will also increase in
the market and this demand creates inflation in the country.
2. Increase in government non development expenditure
2. Increase in government non development expenditure
When
Government spends on non-development project there will be no increase in
production but supply of money increase in the country and price level has also
increase.
3. Deficit financing:
3. Deficit financing:
If central bank adopt the deficit financing
policy there is increase in the money supply in a country due to this policy
price level goes up in the economy.
4. Increase in circulation of money supply
4. Increase in circulation of money supply
If circulation of money increase in the
country price level will be increased in the economy.
5. Effects of Black Money:
5. Effects of Black Money:
When people invest their black money in the
economy the velocity of money increase due to this price level also goes up and
it will create inflation in the economy.
6. Demonstration effect
6. Demonstration effect
As people increase their expenditure due to
demonstration fact demand of goods will be increase and price level will also increase
in the country.
7. Increase in foreign remittances
7. Increase in foreign remittances
If
foreign remittance is increased to a country there will be increase in real
purchasing power of the people. The demand for goods will also increase as
resulting the price level will be increased.
8. Spend thrift society
8. Spend thrift society
If
people of the country are spend thrift they purchase more goods and demand of
things will be increase due to this change in demand price level will also be increase.
9. Increase in cost of imports
9. Increase in cost of imports
If
cost on imports are increased the price of imported goods will also be
increased.
10. Inelastic agriculture production
10. Inelastic agriculture production
If
Agriculture sector yield remain same but demand of goods increase by the people
price of goods will also be increased in the country.
Remedies
to control demand pull inflation
- Control on the population of a country.
- By reducing the circulation of money.
- By controlling the demonstration effect.
- Increase in the production of goods.
- To control the cost of production.
- Reduction in the money supply.
- By controlling the social evil, like monopoly.
- Control on non-development expenditures of government
Author: Nasir Mehmood Ch مصنف: ناصرمحمود چوہدری
Email: Nasirmehmoodch97@gmail.com




.png)

.png)
0 Comments